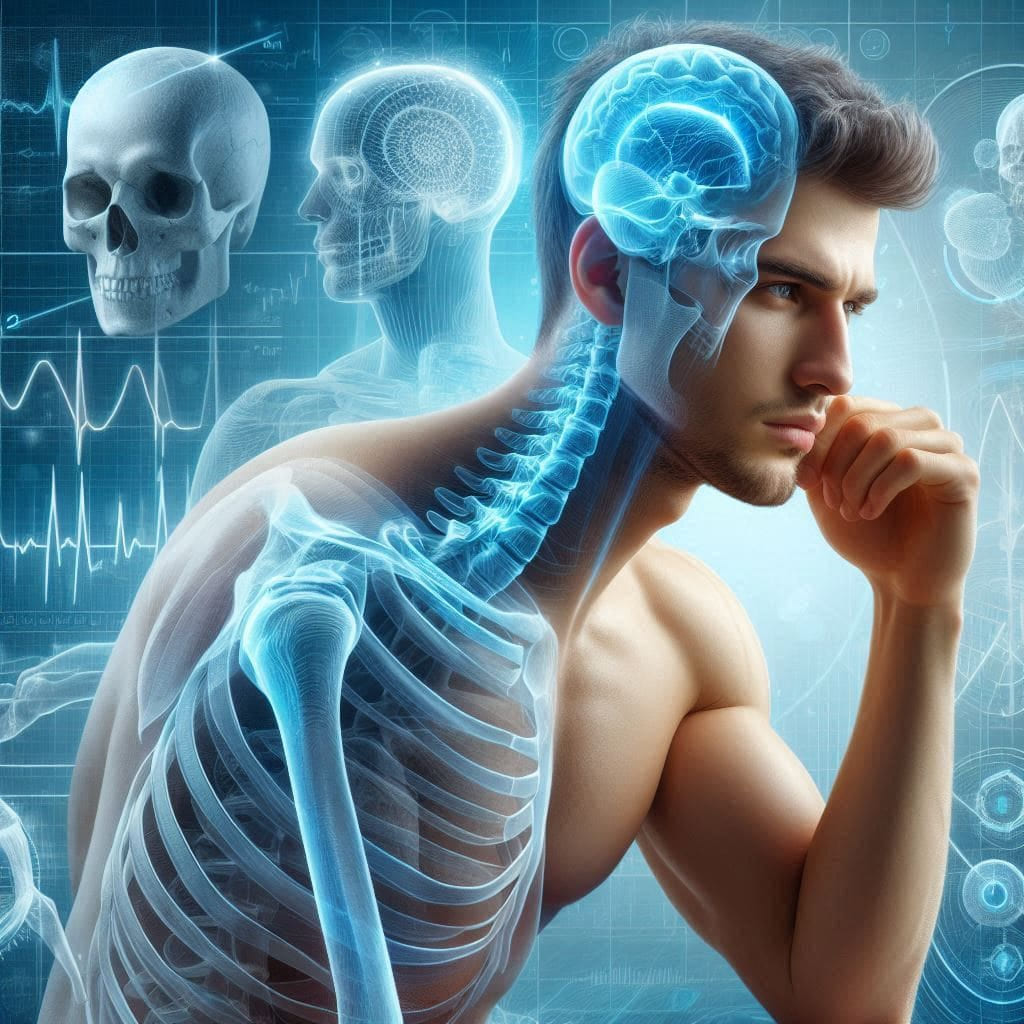
Causes of Low Bone Density
In our modern era, taking care of bone health has become more important than ever, as rates of bone diseases are significantly increasing. Low bone density is one of the health issues that greatly affects quality of life and increases the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. At “Dokki Scan,” we recognize the importance of early detection and accurate diagnosis of these issues to ensure bone health and safety. In this article, we will detail the causes of low bone density, risk factors for osteoporosis, and the role of age and gender in bone weakness.
Bone density is a vital measure of bone strength and health. Low bone density means that bones contain less minerals such as calcium, making them more prone to fractures. There are many causes that can lead to low bone density, which include:
Nutrient Deficiencies: Calcium and vitamin D are essential nutrients that play a significant role in maintaining bone health. Calcium is the main component of bones, and its deficiency can lead to weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures. Vitamin D, on the other hand, helps the body absorb calcium effectively. A deficiency in vitamin D can lead to a decrease in calcium levels in the blood, which negatively affects bone density.
Unbalanced Nutrition: Unbalanced nutrition, including a lack of intake of foods rich in essential minerals and vitamins for bones, can lead to decreased bone density. Not consuming adequate amounts of foods such as dairy products, green leafy vegetables, and nuts can negatively impact bone health.
Unhealthy Lifestyle: A lifestyle characterized by lack of physical activity can lead to weakened bones. Exercise plays a fundamental role in enhancing bone density. Weight-bearing exercises such as walking and weight lifting contribute to strengthening bones. Additionally, unhealthy habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can lead to decreased bone density. Smoking affects the body’s ability to absorb the necessary nutrients for bones, while alcohol can affect bone-building processes.
Medications and Chronic Diseases: Some medications and chronic diseases can lead to low bone density. For example, steroid medications can contribute to calcium loss from bones. Chronic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis can also negatively impact bone health, as they may lead to inflammation and erosion in the joints, affecting bone density.
Risk Factors for Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a medical condition characterized by decreased bone density and increased risk of fractures. There are several risk factors that can lead to osteoporosis, which include:
Genetic Factors: Genetic factors play a significant role in determining the risk of osteoporosis. If you have a family history of bone problems such as osteoporosis, you may be more likely to develop it. Genes affect how calcium is stored in bones and how bone cells regenerate, contributing to determining bone density and strength.
Age: Age is a major risk factor for osteoporosis. As you age, bone density naturally begins to decrease. At a certain stage, the rate of bone loss can exceed the rate of bone formation, leading to a gradual decline in bone density and an increased risk of fractures. This decrease in bone density becomes more pronounced after the age of forty and increases with advancing age.
Gender: Gender also plays a role in the risk of osteoporosis. Women are more likely to develop osteoporosis compared to men, especially after menopause. The hormonal changes that occur during menopause lead to decreased levels of estrogen, a hormone that plays a role in protecting bones and maintaining their density. A deficiency in estrogen can lead to rapid bone density loss.
Nutrition and Dietary Patterns: A diet low in calcium and vitamin D can increase the risk of osteoporosis. Calcium deficiency can lead to weakened bones, while a deficiency in vitamin D affects the body’s ability to absorb calcium. It is essential to consume a balanced diet that includes sources rich in calcium and vitamin D to promote bone health.
The Role of Age and Gender in Bone Weakness
Age: With aging, the process of losing bone density begins naturally. During youth, the body is capable of building strong and dense bones. As aging progresses, bone formation becomes slower than bone loss, leading to a gradual decrease in bone density. After the age of forty, it is crucial to pay more attention to healthcare to maintain bone health.
In older adults, the risks associated with decreased bone density increase, leading to weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures. Hormonal changes and environmental factors such as lack of physical activity and nutrient deficiencies contribute to this deterioration. Therefore, older individuals should take preventive measures such as regular exercise and ensuring adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D.
Gender: Women are more prone to developing osteoporosis compared to men, especially after menopause. During menopause, estrogen levels significantly decrease, leading to increased calcium loss from bones and their weakening. This condition makes women more susceptible to bone problems such as fractures and osteoporosis.
For men, the risk of osteoporosis may be lower compared to women, but this does not mean that men cannot experience bone problems. Men also face decreased bone density with aging, and although hormonal changes may be less severe, other factors such as unhealthy lifestyle and chronic diseases can lead to weakened bones.
The Importance of Early Detection and Monitoring Bone Health
At “Dokki Scan,” we offer advanced services for assessing bone health and measuring bone density. Early detection helps in identifying bone issues before they worsen, allowing for timely measures to maintain bone health. The examination may include advanced techniques such as X-ray (DXA) and CT imaging to provide an accurate assessment of bone condition.
Regular examinations can help track changes in bone density over time, assisting doctors in determining the effectiveness of prescribed treatments and adjusting them if necessary. Additionally, examinations provide valuable information that helps in developing therapeutic strategies and anticipating potential problems.
In conclusion, maintaining bone health requires taking preventive measures that include balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and avoiding unhealthy habits. Regular check-ups at “Dokki Scan” help in monitoring bone health and taking necessary steps to maintain their strength and density.
If you wish to receive a comprehensive assessment of your bone health or need advice on how to improve bone density, we invite you to visit our website at dokki-scan.com or contact us to schedule an appointment. Our team of experts is ready to provide the support and care you need to achieve optimal bone health and ensure a healthy, active life.
Latest Blogs
- All Posts
- Blog