How Long Does a Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan Take?
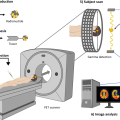
In the modern medical diagnostic world, imaging techniques play a crucial role in accurately identifying and monitoring medical conditions. Among these techniques, Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans stand out as a powerful tool for detecting a wide range of diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders. In this article, we will review the duration of a PET scan, its procedural stages, and the factors that affect the duration of the scan, within the services offered by the Dokki Scan at their website dokki-scan.com.
How Long Does a PET Scan Take?
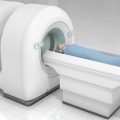
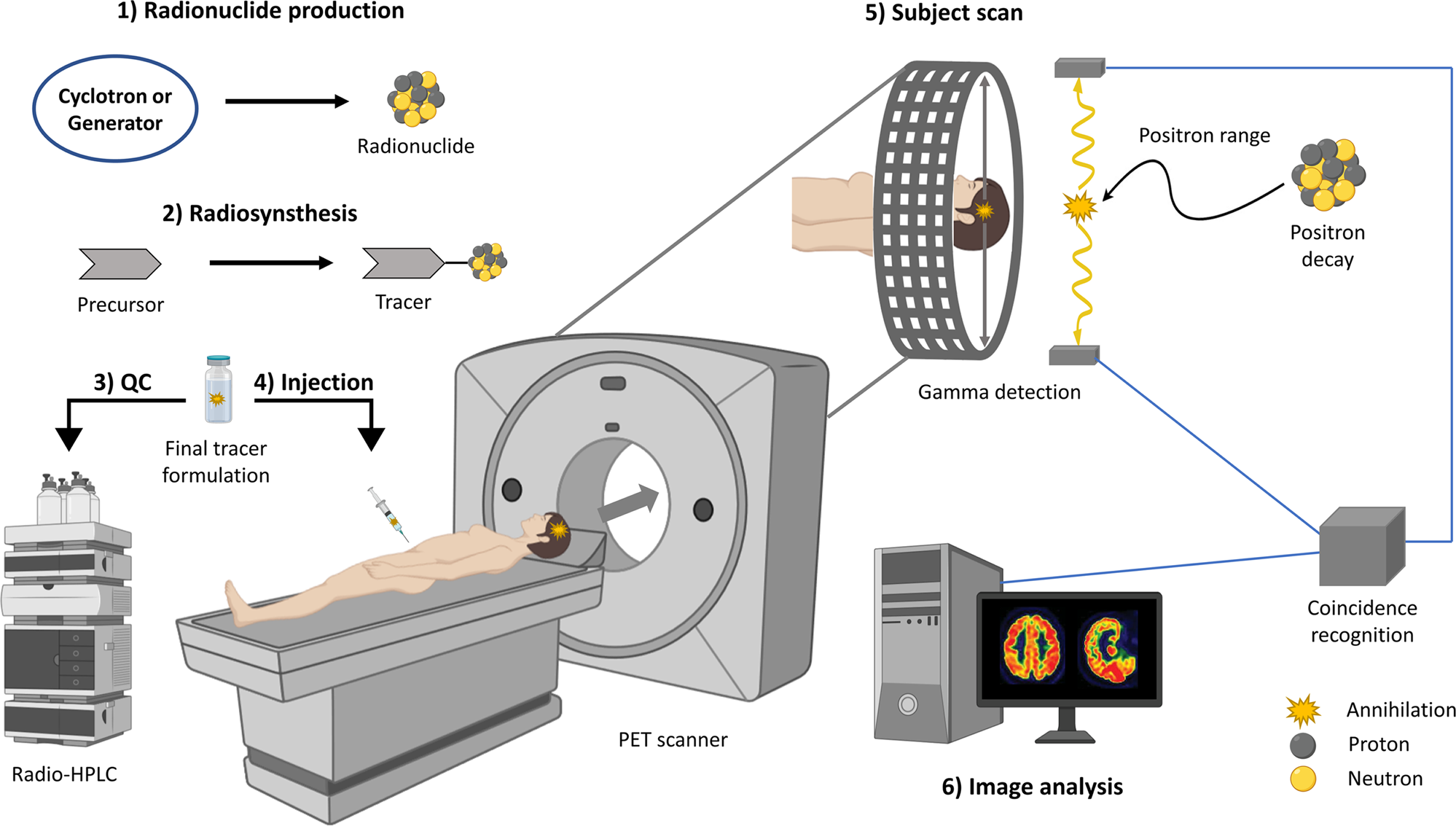
A PET scan typically takes about 1.5 to 2 hours, although this time can vary depending on several factors. These factors include the type of scan required, the patient’s health condition, and the technology used at the medical center. It is important for patients to understand that the actual scanning part, where images are captured, may only take about 20 to 30 minutes, but the preparation and waiting for the radiotracer to distribute in the body extend the total time.
Stages of the Procedure
Preparation for the Scan
Before starting a PET scan, there are some preparations that the patient must undertake to ensure accurate results. The patient may be asked to fast for 4 to 6 hours before the scan, avoiding caffeine or sugary foods. The patient should also inform the doctor of any medications they are taking or health conditions that might affect the scan.
Injection of the Radiotracer
At the beginning of the scan, the patient is injected with a radiotracer called “fluorodeoxyglucose” (FDG). This substance needs some time to spread through the body and accumulate in areas with high cellular activity, such as cancerous tumors. This stage usually takes from 30 to 60 minutes, during which the patient is asked to relax and avoid excessive movement to prevent uneven distribution of the radiotracer.
Main Scanning Procedure
After the radiotracer has spread, the patient is positioned in the PET scan machine. The patient is placed in a comfortable position and asked to remain still while images are captured. This part of the scan takes about 20 to 30 minutes, during which images are taken from multiple angles to provide a comprehensive and detailed view of the targeted areas.
Post-Scan
After the scan is completed, the patient can return to their normal daily activities. They may be advised to drink plenty of water to help flush the radiotracer from their body more quickly. The patient should follow any special instructions provided by the doctor or scanning team to ensure the best possible results.
Before starting a PET scan, there are some preparations that the patient must undertake to ensure accurate results. The patient may be asked to fast for 4 to 6 hours before the scan, avoiding caffeine or sugary foods. The patient should also inform the doctor of any medications they are taking or health conditions that might affect the scan.
Injection of the Radiotracer
At the beginning of the scan, the patient is injected with a radiotracer called “fluorodeoxyglucose” (FDG). This substance needs some time to spread through the body and accumulate in areas with high cellular activity, such as cancerous tumors. This stage usually takes from 30 to 60 minutes, during which the patient is asked to relax and avoid excessive movement to prevent uneven distribution of the radiotracer.
Main Scanning Procedure
After the radiotracer has spread, the patient is positioned in the PET scan machine. The patient is placed in a comfortable position and asked to remain still while images are captured. This part of the scan takes about 20 to 30 minutes, during which images are taken from multiple angles to provide a comprehensive and detailed view of the targeted areas.
Post-Scan
After the scan is completed, the patient can return to their normal daily activities. They may be advised to drink plenty of water to help flush the radiotracer from their body more quickly. The patient should follow any special instructions provided by the doctor or scanning team to ensure the best possible results.
Factors Affecting the Scan Duration
Type of Scan Required
The duration of a PET scan varies based on the type of scan required. For example, scans for cancer detection might take longer compared to scans for evaluating heart or neurological functions.
Patient’s Health Condition
The patient’s health condition plays a significant role in determining the scan duration. Patients with complex medical conditions or those taking certain medications may need more time for preparation and for the radiotracer to distribute throughout the body.
Technology and Equipment Used
The technology used at the medical center affects the speed and accuracy of the scan. Centers with modern and advanced equipment can perform the scan faster and more efficiently, reducing the overall duration.
Medical Staff Efficiency
The experience and efficiency of the medical staff play a vital role in expediting the scan process. Well-trained staff can conduct the scan quickly and effectively, ensuring patient comfort and accurate results.
The duration of a PET scan varies based on the type of scan required. For example, scans for cancer detection might take longer compared to scans for evaluating heart or neurological functions.
Patient’s Health Condition
The patient’s health condition plays a significant role in determining the scan duration. Patients with complex medical conditions or those taking certain medications may need more time for preparation and for the radiotracer to distribute throughout the body.
Technology and Equipment Used
The technology used at the medical center affects the speed and accuracy of the scan. Centers with modern and advanced equipment can perform the scan faster and more efficiently, reducing the overall duration.
Medical Staff Efficiency
The experience and efficiency of the medical staff play a vital role in expediting the scan process. Well-trained staff can conduct the scan quickly and effectively, ensuring patient comfort and accurate results.
Patient Tips and Guidelines
Proper Preparation
Proper preparation before the scan can help reduce the time spent and ensure accurate results. Here are some important tips for preparation:
Fasting: The patient may need to fast for 4 to 6 hours before the scan to lower blood glucose levels, which helps improve scan accuracy.
Avoiding Caffeine and Sugary Foods: The patient should avoid caffeine and sugary foods before the scan, as these can affect the distribution of the radiotracer in the body.
Reporting Medications: The patient should inform the medical team about all medications they are taking, including prescribed and over-the-counter drugs, as these may affect scan results.
Communicating with Medical Staff
Good communication with the medical team is essential for preparation. Here are some points to consider:
Asking Questions: Do not hesitate to ask any questions about the scan, including its stages and any special instructions that need to be followed.
Reporting Allergies: If you have any allergies, especially to radiotracers, you should inform the medical team.
Relaxation: Try to relax before and during the scan, as stress can affect scan results.
Rest and Good Sleep
Getting enough rest and sleep before the scan can help improve the accuracy of the results. Here are some tips for achieving this:
Early Bedtime: Try to go to bed early on the night before the scan to ensure a good night’s sleep.
Avoiding Stimulants: Avoid stimulants like caffeine before bed to ensure a peaceful and restful sleep.
Relaxation: Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing to reduce stress and anxiety before the scan.
Proper preparation before the scan can help reduce the time spent and ensure accurate results. Here are some important tips for preparation:
Fasting: The patient may need to fast for 4 to 6 hours before the scan to lower blood glucose levels, which helps improve scan accuracy.
Avoiding Caffeine and Sugary Foods: The patient should avoid caffeine and sugary foods before the scan, as these can affect the distribution of the radiotracer in the body.
Reporting Medications: The patient should inform the medical team about all medications they are taking, including prescribed and over-the-counter drugs, as these may affect scan results.
Communicating with Medical Staff
Good communication with the medical team is essential for preparation. Here are some points to consider:
Asking Questions: Do not hesitate to ask any questions about the scan, including its stages and any special instructions that need to be followed.
Reporting Allergies: If you have any allergies, especially to radiotracers, you should inform the medical team.
Relaxation: Try to relax before and during the scan, as stress can affect scan results.
Rest and Good Sleep
Getting enough rest and sleep before the scan can help improve the accuracy of the results. Here are some tips for achieving this:
Early Bedtime: Try to go to bed early on the night before the scan to ensure a good night’s sleep.
Avoiding Stimulants: Avoid stimulants like caffeine before bed to ensure a peaceful and restful sleep.
Relaxation: Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing to reduce stress and anxiety before the scan.
Medical Benefits of PET Scans
Early Disease Detection
PET scans are powerful tools for early detection of various diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders. This scan can identify changes in cellular functions before symptoms appear, allowing for early treatment and improved chances of recovery.
Cancer: PET scans can identify cancerous tumors and assess their spread, aiding in effective treatment planning.
Heart Disease: The scan can evaluate blood flow to the heart muscle and detect any narrowing of the coronary arteries.
Neurological Disorders: The scan helps diagnose neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s by detecting changes in brain activity.
Evaluating Treatment Effectiveness
PET scans can play a crucial role in assessing the effectiveness of various treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer. By comparing images taken before and after treatment, doctors can determine whether the treatment is improving the condition or not.
Assessing Treatment Response: The scan can be used to determine whether tumors are responding to chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Adjusting Treatment Plans: Based on the scan results, doctors can adjust treatment plans to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Personalized Treatment
PET scans are important for tailoring treatment to each patient based on their unique condition. By providing accurate information about the extent and activity of the disease, doctors can design personalized treatment plans for each patient.
Disease Staging: The scan helps accurately stage the disease, allowing doctors to select the most appropriate treatment.
Customized Care: Understanding the patient’s condition precisely enables the development of a tailored treatment plan that meets their individual needs.
Summary of the PET Scan Duration
In conclusion, a Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan is essential for accurate diagnosis of many medical conditions, including cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders. The duration of the scan depends on several factors but generally includes three main stages:
Preparation: Requires fasting and prior preparation for 4 to 6 hours.
Radiotracer Injection: Takes about 15 minutes, followed by a waiting period of 30 to 60 minutes for the radiotracer to spread throughout the body.
Imaging: The actual imaging process takes between 30 to 45 minutes.
Overall, the total time spent at the center may range from two to three hours, depending on the preparation speed and the radiotracer’s distribution. This time reflects the importance of precision in performing the scan and ensuring reliable results that aid in accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning.
PET scans are powerful tools for early detection of various diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders. This scan can identify changes in cellular functions before symptoms appear, allowing for early treatment and improved chances of recovery.
Cancer: PET scans can identify cancerous tumors and assess their spread, aiding in effective treatment planning.
Heart Disease: The scan can evaluate blood flow to the heart muscle and detect any narrowing of the coronary arteries.
Neurological Disorders: The scan helps diagnose neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s by detecting changes in brain activity.
Evaluating Treatment Effectiveness
PET scans can play a crucial role in assessing the effectiveness of various treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer. By comparing images taken before and after treatment, doctors can determine whether the treatment is improving the condition or not.
Assessing Treatment Response: The scan can be used to determine whether tumors are responding to chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Adjusting Treatment Plans: Based on the scan results, doctors can adjust treatment plans to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Personalized Treatment
PET scans are important for tailoring treatment to each patient based on their unique condition. By providing accurate information about the extent and activity of the disease, doctors can design personalized treatment plans for each patient.
Disease Staging: The scan helps accurately stage the disease, allowing doctors to select the most appropriate treatment.
Customized Care: Understanding the patient’s condition precisely enables the development of a tailored treatment plan that meets their individual needs.
Summary of the PET Scan Duration
In conclusion, a Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan is essential for accurate diagnosis of many medical conditions, including cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders. The duration of the scan depends on several factors but generally includes three main stages:
Preparation: Requires fasting and prior preparation for 4 to 6 hours.
Radiotracer Injection: Takes about 15 minutes, followed by a waiting period of 30 to 60 minutes for the radiotracer to spread throughout the body.
Imaging: The actual imaging process takes between 30 to 45 minutes.
Overall, the total time spent at the center may range from two to three hours, depending on the preparation speed and the radiotracer’s distribution. This time reflects the importance of precision in performing the scan and ensuring reliable results that aid in accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning.
Dokki Scan Services
At Dokki Scan, we offer a wide range of advanced medical imaging services, including Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans. We are committed to providing the highest levels of medical care using the latest technologies to ensure patient comfort and accurate, effective diagnoses. Our team of specialized doctors and trained technicians is ready to offer support and guidance to patients at every step of the scan process.
Latest Blogs
- All Posts
- Blog